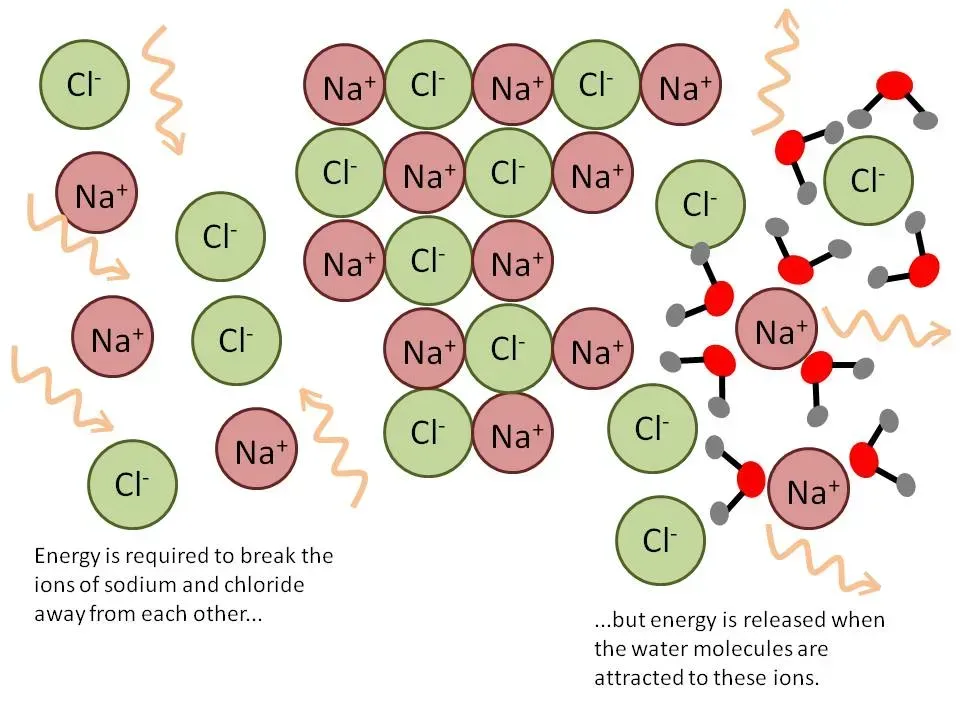
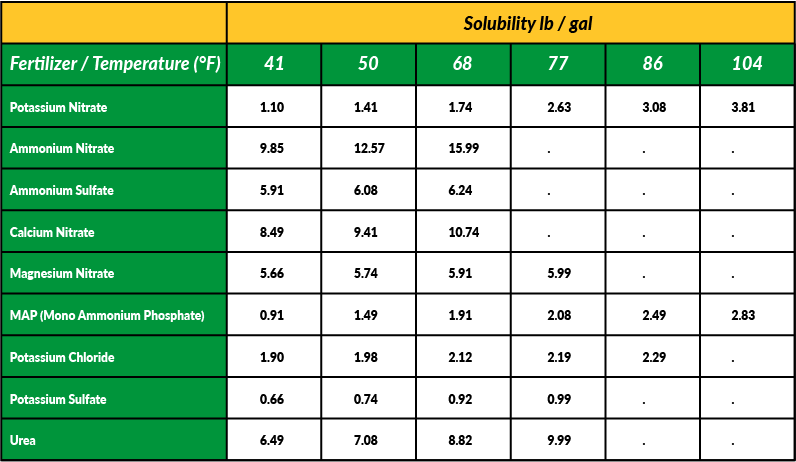
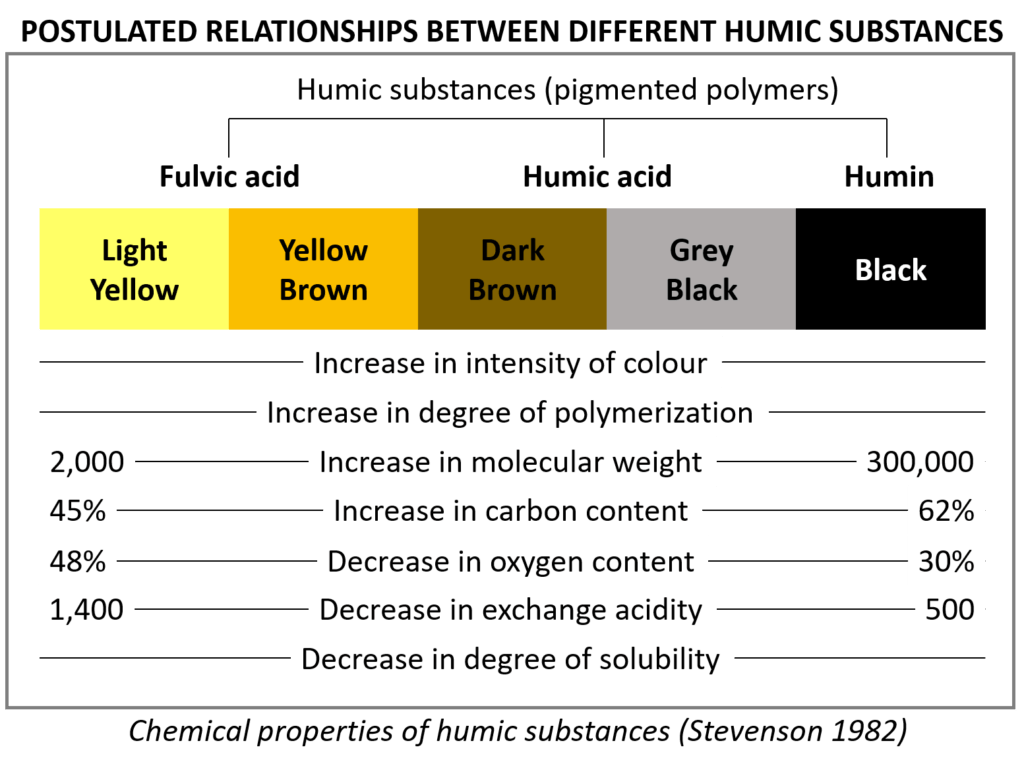
One of the most important concepts in fertilizer chemistry and plant nutrition is “solubility.” In the plant sciences, solubility is defined as how readily nutrients are dissolved in water and can be taken up by plants. There are many factors that can affect the solubility of a nutrient, including but not limited to chemical structure, ion charge, temperature, and pressure. pH can also have a profound impact on the solubility of nutrients; this is because different types of nutrients in a solution/soil colloid will tend to attract or repel each other based on their chemical properties. Sometimes it is beneficial to fertilize plants with highly soluble nutrients; sometimes it’s detrimental. In this feature, well examine the topic of solubility in greater detail so that you have a better grasp as to how the nutrients you choose to fertilizer with will 1.) react with the environment and 2.) affect plant health.
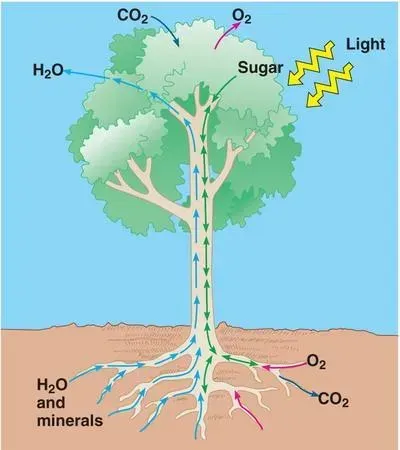
Before we learn more about the solubility of common fertilizer chemistries, let’s take a moment to review basic plant physiology. As we will see, if nutrients were not capable of being dissolved in water, plant life would not be possible.